Pomodoro Technique
The Pomodoro Technique is a time management method that helps you get things done in an efficient and effective way. It was created by Francesco Cirillo in the late 1980s, when he used a kitchen timer shaped like a tomato (pomodoro is Italian for “tomato”) to break down his work into intervals of 25 minutes with five-minute breaks between each interval. This technique has since been adopted by many people around the world as an effective way to manage their time and increase productivity.
The Pomodoro Technique encourages users to focus on one task at a time without distractions, and it allows them to track how much time they spend working on tasks so they can better estimate how long future tasks will take.
By breaking down large projects into smaller chunks, Pomodoro users are able to stay focused while avoiding burnout or fatigue from focusing too long on any one thing. Additionally, Pomodoro users are encouraged to take regular breaks throughout their day which helps keep them refreshed and motivated throughout their workday.
If you’re looking for an easy way to improve your productivity and maximize your efficiency during the day, then look no further than the Pomodoro Technique! This simple yet powerful tool can help you get more done in less time and keep your energy levels up while doing it. Try it out today and see how Pomodoro can help you get things done!
What is the Pomodoro Technique?
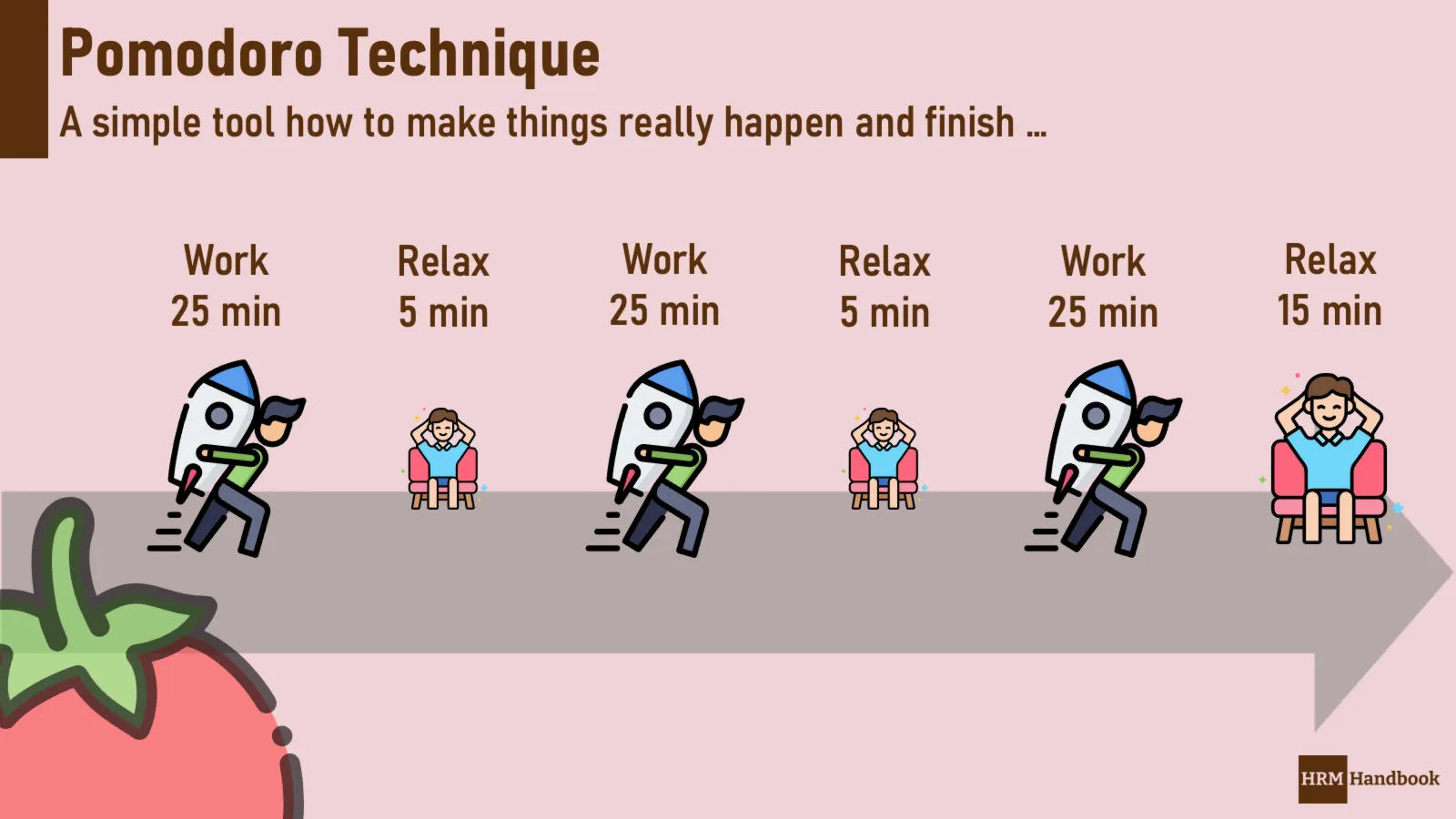
For those looking for an effective way to manage their time, the Pomodoro Technique is a great option. This system calls for 25-minute stretches of concentrated work that are then followed by five-minute breaks. After four consecutive pomodori (the Italian word for tomatoes), longer 15 - 30 minute breaks should be taken. So why tomato? Because when this method was created in the 80s, it used real kitchen timers shaped like a tomato!
In the late 1980s, Francesco Cirillo - a university student-turned-developer and entrepreneur - revolutionized productivity with his Pomodoro Technique. The concept was birthed from a simple tomato-shaped kitchen timer which he used to regulate his study schedule.
At first, he tested various lengths of work periods - from two minutes to one hour - but discovered they were excessively long and difficult to keep his attention. After further testing, he decided that 25-minute Pomodoro sessions best suited his needs.
Cirillo observed how to turn time into an ally rather than a worry. Through the Pomodoro Technique, people learn to concentrate more by limiting the length of their attention span and taking regular breaks from the task at hand. It also helps them surmount any tendencies they may have towards procrastination or multitasking that are proven to lower productivity levels.
Compare Pomodoro Technique to other GTD techniques
The Pomodoro Technique is a time management method developed by Francesco Cirillo in the late 1980s, while Getting Things Done (GTD) is a productivity system created by David Allen. Both methods aim to improve productivity and efficiency, but they approach time management and task completion differently. Here’s a comparison of the Pomodoro Technique to other GTD techniques:
Pomodoro Technique:
- Focuses on time management and breaking work into short intervals (usually 25 minutes) called “Pomodoros,” followed by a short break (typically 5 minutes). After four Pomodoros, a longer break (15-30 minutes) is taken.
- Aims to improve focus and concentration by minimizing distractions and maintaining a consistent workflow.
- Can be applied to various tasks and projects, regardless of their complexity.
- Provides immediate feedback on progress by tracking completed Pomodoros.
GTD techniques:
- GTD is a holistic system that encompasses multiple techniques, such as capturing ideas, processing them, organizing them into actionable steps, reviewing progress, and focusing on the appropriate next action.
- GTD starts with capturing all ideas, tasks, and projects in a trusted external system, such as a notebook, app, or digital organizer.
- Tasks are processed by determining whether they are actionable and, if so, breaking them down into the smallest possible steps.
- Tasks are organized into lists based on context, priority, or due date, making it easier to decide what to work on next.
- The GTD system promotes regular reviews of tasks and projects to ensure that nothing slips through the cracks.
In summary, the Pomodoro Technique primarily focuses on time management and maintaining focus, while GTD techniques are a comprehensive productivity system that covers various aspects of task and project management. The two methods can be used in conjunction with each other; for example, you can use GTD techniques to organize tasks and projects, and then apply the Pomodoro Technique to maintain focus and make consistent progress on those tasks.
Pomodoro Technique Benefits (compared with other GTD techniques)
The Pomodoro Technique and GTD techniques each offer unique benefits, and they can be complementary when used together. Here are some of the benefits of the Pomodoro Technique compared to other GTD techniques:
- Time management and focus: The Pomodoro Technique emphasizes time management by breaking work into short, focused intervals (Pomodoros) followed by short breaks. This structure helps individuals maintain focus and minimize distractions, which can lead to increased productivity. In contrast, GTD techniques focus on organizing tasks and managing projects. While GTD can help with time management through task prioritization, it does not provide a specific time-based structure like the Pomodoro Technique.
- Simple and easy to implement: The Pomodoro Technique is relatively simple and easy to implement, requiring only a timer and a basic understanding of its principles. This simplicity makes it accessible to a wide range of users, even those with no prior experience with time management methods. GTD techniques, while highly effective, can be more complex and require more time to learn and set up. Individuals need to develop a trusted system for capturing, processing, organizing, and reviewing tasks.
- Reduces burnout and mental fatigue: The regular breaks built into the Pomodoro Technique help reduce the risk of burnout and mental fatigue. By allowing time for rest and rejuvenation, individuals can maintain a sustainable work pace throughout the day. While GTD techniques do encourage users to break tasks into manageable steps, they do not specifically address the need for regular breaks to maintain mental well-being.
- Encourages a sense of accomplishment: The Pomodoro Technique provides immediate feedback on progress by tracking completed Pomodoros. This sense of accomplishment can boost motivation and make it easier to stay engaged with tasks. GTD techniques, while effective in organizing and prioritizing tasks, do not have a built-in system for tracking progress in the same way.
- Adaptable to various tasks and projects: The Pomodoro Technique can be applied to a wide range of tasks and projects, regardless of complexity. The method remains the same, and individuals can adjust the number of Pomodoros dedicated to each task as needed. GTD techniques are also adaptable, but they require more customization for different tasks and projects due to their focus on organizing and processing tasks.
Overall, the Pomodoro Technique offers benefits such as improved time management, focus, simplicity, reduced burnout, and adaptability. While GTD techniques excel in task organization and prioritization, they do not specifically address time management and focus in the same way. Combining the Pomodoro Technique with GTD techniques can lead to a comprehensive and effective productivity system.
Pomodoro Technique Weaknesses
While the Pomodoro Technique offers several benefits, it also has some weaknesses and limitations. Here are some of the potential drawbacks of the method:
- Inflexibility with time intervals: The standard Pomodoro interval of 25 minutes followed by a 5-minute break might not be suitable for everyone or every task. Some tasks may require longer periods of uninterrupted focus, while others may need shorter bursts of attention.
- Interruptions and distractions: The Pomodoro Technique assumes that individuals can work undisturbed for the duration of a Pomodoro. However, in some environments, interruptions and distractions are inevitable, making it difficult to complete a full Pomodoro without losing focus.
- Incompatibility with certain tasks or jobs: Some tasks or jobs do not lend themselves well to the Pomodoro Technique, particularly those that require constant collaboration, frequent communication, or immediate responsiveness.
- Overemphasis on time rather than tasks: The Pomodoro Technique focuses on managing time rather than tasks, which may lead to an overemphasis on the number of Pomodoros completed rather than the actual progress made on tasks.
- Pressure to perform within time constraints: For some individuals, the strict time constraints imposed by the Pomodoro Technique can create stress and anxiety, making it harder to focus and complete tasks.
- Difficulty adapting to changing priorities or emergencies: The Pomodoro Technique encourages working on predetermined tasks in a structured manner. However, this approach may not be as effective when dealing with unexpected emergencies or changing priorities that require immediate attention.
- Inadequate long-term planning and task organization: The Pomodoro Technique primarily focuses on short-term time management and does not provide a comprehensive system for long-term planning, task organization, or project management like GTD techniques.
While the Pomodoro Technique has its weaknesses, many of these limitations can be mitigated through customization or by combining it with other productivity methods, such as GTD techniques, to create a more comprehensive and flexible time management system.
What are the fundamentals of the Pomodoro Technique?
The Pomodoro Technique can also help individuals develop more efficient work habits, as it encourages them to break down tasks into smaller, manageable chunks that can be focused on for a set amount of time. This means that instead of feeling overwhelmed by a large, looming task, Pomodoro users can tackle it bit by bit. Not only does this improve focus and concentration, but it also helps Pomodoro users stay on track as they get things done.
The Pomodoro Technique generally involves the following steps:
- Decide on a task to be completed.
- Set the Pomodoro timer for 25 minutes and work on the task until the timer rings.
- Take a short break (5 minutes) to give the mind time to rest.
- After 4 Pomodoros, take a longer break (15-30 minutes).
- Repeat the process until the task is completed or progress on it is significant enough for it to be marked as “done” in Pomodoro’s tracking system.
By dividing projects into Pomodoros, people can concentrate more attentively and minimize diversions to finish their tasks quicker. Furthermore, regular users of the Pomodoro Technique can easily monitor their progress with a straightforward chart to remain motivated and evaluate how much they have achieved.
With proficient time management, people are capable of achieving more in a shorter period and feeling proud of their accomplishments, all while avoiding the threat of burnout.
Pomodoro Technique Processes and Routines
The Pomodoro Technique can be broken down into various processes to help individuals and teams manage their time effectively, increase productivity, and maintain focus. Here’s a breakdown of the Pomodoro processes:
- Pomodoro Internal Process: This process focuses on developing an effective relationship with time. By understanding the limitations of time and the need for balance between work and breaks, individuals can become more conscious of how they spend their time and adjust their habits to optimize productivity.
- Pomodoro Core Process: The core process aims to help individuals focus on tasks to reach their goals with less effort. By dividing work into manageable intervals (Pomodoros) and taking short breaks in between, individuals can maintain their concentration and minimize distractions, resulting in more efficient task completion.
- Pomodoro Daily Process: Implementing a daily routine with the Pomodoro Technique can help individuals improve their daily work process and complete multiple tasks more effectively. By consistently following the Pomodoro intervals and breaks throughout the day, individuals can maintain a steady workflow and reduce the risk of burnout.
- Pomodoro Weekly Process: A weekly routine based on the Pomodoro Technique can help individuals organize their time more efficiently and achieve multiple goals. By planning tasks for the week and allocating Pomodoros to each task, individuals can prioritize their work and ensure that they stay on track to meet their deadlines.
- Pomodoro Team Process: Adapting the Pomodoro Technique to a team setting can help improve collaboration, communication, and overall productivity. Teams can set shared goals, break tasks into Pomodoros, and coordinate their work schedules to ensure everyone is working in sync. Regular check-ins and progress reviews can help teams stay accountable and make any necessary adjustments to their workflow.
By incorporating these various Pomodoro processes, both individuals and teams can benefit from increased productivity, focus, and time management.
Pomodoro Technique Best Practices
To make the most of the Pomodoro Technique, it’s essential to follow some best practices. These practices will help you maximize productivity, maintain focus, and avoid burnout while using the technique:
- Customize the Pomodoro intervals: While the traditional Pomodoro interval is 25 minutes of work followed by a 5-minute break, you may find that different intervals work better for you. Experiment with various work and break durations to determine the optimal interval for your needs and tasks.
- Minimize distractions: Before starting a Pomodoro, take steps to minimize potential distractions. Close unnecessary browser tabs, silence your phone, or use noise-cancelling headphones if needed. Inform colleagues or family members that you’ll be working uninterrupted for the duration of the Pomodoro.
- Prioritize tasks: Before starting your workday, create a list of tasks you want to complete and prioritize them based on importance and urgency. Allocate Pomodoros to each task, and use these estimates to plan your day.
- Break tasks into smaller subtasks: If you’re working on a large or complex task, break it down into smaller, manageable subtasks. This will make it easier to estimate the number of Pomodoros needed and provide a sense of accomplishment as you complete each subtask.
- Use breaks effectively: During your short breaks, engage in activities that allow your brain to rest and recharge, such as stretching, taking a short walk, or engaging in deep breathing exercises. Avoid activities that require significant mental effort or might lead to further distractions.
- Take longer breaks after multiple Pomodoros: After completing four Pomodoros, take a longer break (15-30 minutes) to fully recharge and maintain productivity throughout the day. Use this time to engage in activities that help you relax and disconnect from work.
- Track your progress: Keep a record of the number of Pomodoros you complete each day and the tasks you’ve accomplished. Tracking your progress can help you identify patterns, improve time management, and maintain motivation.
- Adjust as needed: Continuously evaluate the effectiveness of the Pomodoro Technique in your workflow and make adjustments as needed. This may include altering the length of intervals, reprioritizing tasks, or changing your work environment to minimize distractions.
- Combine with other productivity techniques: For a more comprehensive productivity system, consider combining the Pomodoro Technique with other methods, such as GTD techniques. This can help address the limitations of the Pomodoro Technique and improve overall task organization, prioritization, and long-term planning.
By incorporating these best practices, you can optimize the Pomodoro Technique to enhance your productivity, focus, and overall time management.
Recommended Pomodoro Technique Applications
There are several Pomodoro Technique applications available for various platforms, including Mac, iPhone, Windows, and Android. Here are some of the best apps for each platform, keeping in mind that app ratings may change over time as developers release updates and users provide feedback:
Apple Macintosh
Focus (Rating: 4.5/5): Focus is a popular Pomodoro app for macOS with a clean interface and customizable intervals. It allows users to set goals, track progress, and integrate with other productivity apps like Trello and Todoist.
Be Focused (Rating: 4.5/5): Be Focused combines a Pomodoro timer with a task manager, allowing users to create task lists, set goals, and track progress. It also offers customizable intervals and synchronization between macOS and iOS devices.
iPhone
Forest (Rating: 4.8/5): Forest is a unique Pomodoro app that gamifies productivity by growing virtual trees as you stay focused on your work. The app is available for both iOS and Android and offers customizable intervals, task management, and progress tracking.
Focus Keeper (Rating: 4.6/5): Focus Keeper is a simple Pomodoro timer for iOS devices with customizable intervals, a color-coded interface, and progress tracking. It also offers statistics to help users analyze their productivity over time.
Windows
- Pomodone (Rating: 4.2/5): Pomodone is a Pomodoro app for Windows that integrates with popular task management services like Asana, Trello, and Todoist. It offers customizable intervals, progress tracking, and analytics.
- Focus 10 (Rating: 4.0/5): Focus 10 is a minimalistic Pomodoro timer for Windows 10 that includes customizable intervals, progress tracking, and a clean interface. It can run in the background or be pinned to the taskbar for easy access.
Android:
- Tide (Rating: 4.8/5): Tide is a productivity app for Android that combines the Pomodoro Technique with ambient sounds to create a focused work environment. It offers customizable intervals, progress tracking, and daily/weekly/monthly productivity analysis.
- Brain Focus (Rating: 4.6/5): Brain Focus is a Pomodoro timer for Android with a simple interface and customizable intervals. It includes task management, progress tracking, and the ability to pause and resume sessions.
Please note that the ratings mentioned here are based on user feedback and might change over time. Additionally, some of these apps may have paid features or in-app purchases for advanced functionality. Always check for the most up-to-date ratings and reviews before choosing an app to ensure it meets your needs and preferences.
And finally … Pomodoro Technique Tips and Tricks
The Pomodoro Technique is a great way to manage time efficiently. By setting Pomodoro intervals and taking regular breaks, individuals can work on tasks more effectively and stay focused. To ensure a seamless transition between Pomodoros, it is important to set aside time for recap and review.
At the end of each Pomodoro, or work interval, set aside time to review your progress and make any necessary adjustments. This will help you stay on track with the Pomodoro Technique and ensure that you meet your goals.
To stay productive, individuals must guard their pomodoro against both internal and external interruptions. Refrain from examining emails, social network accounts, meteorological forecasts, news stories or any other distractions that can draw your attention away from the current assignment.
Practitioners of the Pomodoro Technique may use different periods for task and break segments. During those breaks, it is especially important to choose an activity that differs significantly from your current task in order to maximize productivity.