Competency Model
In the ever-evolving world of business, organizations must stay ahead of the curve to remain competitive and successful. One critical aspect of achieving this is by ensuring that employees are equipped with the right skills, knowledge, and behaviors to excel in their roles. A well-designed competency model can play a pivotal role in aligning an organization’s workforce with its strategic goals. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of competency models, exploring their significance, advantages, and how they can be created and implemented effectively within an organization.
Competency models have gained increasing prominence in recent years as organizations recognize their potential to drive performance and boost employee engagement. By providing a clear framework for the key competencies required in specific roles, these models serve as invaluable tools for human resources professionals. They can aid in enhancing various aspects of talent management, from recruitment and selection to employee development and performance management.
The successful implementation of a competency model can have far-reaching benefits for organizations and employees alike. For organizations, a well-designed competency model can streamline recruitment processes, enhance training and development initiatives, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. For employees, having a clear understanding of the competencies required for their roles can lead to better performance, increased engagement, and more opportunities for growth and development.
Developing and implementing a competency model, however, is not a one-size-fits-all process. It requires a thorough understanding of the organization’s unique culture, values, and strategic goals. Furthermore, it demands a commitment to ongoing evaluation and refinement to ensure that the model remains relevant and effective in the face of changing business conditions and workforce needs.
In the following sections, we’ll provide a comprehensive overview of competency models, exploring their core components, benefits, and how they can be tailored to meet the specific needs of an organization. By understanding the potential of these powerful tools, human resources professionals can unlock new opportunities to drive performance, enhance employee engagement, and ultimately contribute to the long-term success of their organizations.
What is a competency model?
A competency model is a structured framework that identifies and organizes the essential skills, knowledge, and behaviors required for success in a specific role or job function within an organization. These models serve as a comprehensive guide for human resources professionals, managers, and employees, offering a clear understanding of the expectations and requirements of various positions. By defining the competencies needed for effective performance, organizations can better align their workforce with strategic goals, streamline talent management processes, and facilitate overall organizational success.
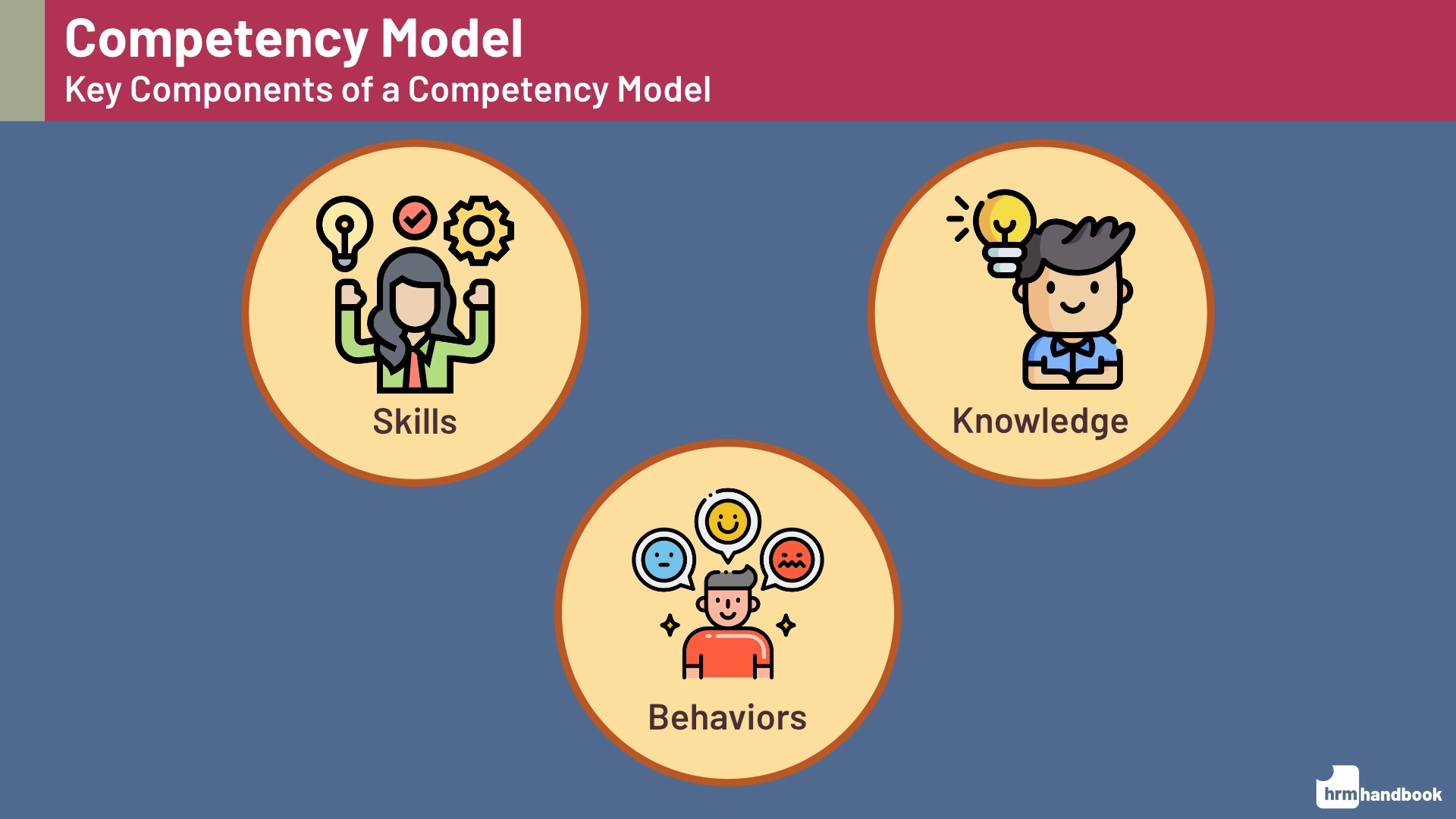
The components of a competency model can be broadly classified into three categories:
Skills: These are the specific abilities or proficiencies that employees must possess to perform their job effectively. Skills can be technical or soft in nature. Technical skills are job-specific, such as programming languages for a software developer, while soft skills, like communication and teamwork, are transferable across various job roles and industries.
Knowledge: This refers to the understanding and expertise that employees must have in a particular domain, subject matter, or industry. Knowledge may encompass information about company policies, industry regulations, best practices, and emerging trends that impact the organization or job function.
Behaviors: These are the actions, attitudes, and work styles that employees must exhibit to be successful in their roles. Behaviors encompass personal traits, such as adaptability, problem-solving, and leadership, which contribute to an individual’s ability to navigate complex situations and effectively collaborate with colleagues.
Competency models can vary in complexity and scope, depending on the organization’s size, industry, and strategic objectives. Some models may focus solely on the core competencies required for a specific job function, while others may encompass a more comprehensive approach, addressing competencies at various organizational levels or across multiple job functions. In general, an effective competency model should be tailored to the organization’s unique needs, taking into consideration factors such as the company culture, values, and strategic goals.
In summary, a competency model is a structured framework that outlines the essential skills, knowledge, and behaviors necessary for success in a particular role or job function. By defining these competencies, organizations can better align their workforce with strategic objectives, enhance talent management processes, and facilitate overall success. Competency models serve as a valuable tool for human resources professionals, managers, and employees alike, providing a clear roadmap for performance expectations, employee development, and organizational growth.
Benefits of Competency Models
Competency models offer numerous advantages for organizations and employees alike. By defining and organizing the essential skills, knowledge, and behaviors required for success in specific roles or job functions, these models facilitate effective talent management and support the achievement of strategic objectives. Here is a detailed explanation of the key benefits of competency models:
Improved hiring and selection processes: By outlining the competencies needed for a specific role, competency models can inform job descriptions, interview questions, and candidate assessment tools. This enables organizations to streamline their recruitment efforts and select candidates who possess the necessary skills, knowledge, and behaviors to succeed in the position, ultimately reducing turnover and improving overall workforce quality.
Targeted employee development: Competency models help organizations identify skill gaps among their workforce, allowing for the creation of tailored training and development programs that address these gaps. By focusing on the areas that have the most significant impact on performance, organizations can optimize their training resources and enable employees to enhance their skills and knowledge in areas most relevant to their roles.
Enhanced performance management: Competency models provide a clear and objective framework for evaluating employee performance. By aligning performance evaluation criteria with the competencies identified in the model, organizations can promote transparency and fairness in the assessment process. This leads to more effective performance management, feedback, and ultimately, improved employee performance.
Increased employee engagement and retention: Employees who understand the expectations of their roles and have access to opportunities for growth and development are more likely to be engaged in their work. Competency models help employees identify their strengths and areas for improvement, enabling them to chart a clear path for professional development. This not only enhances employee satisfaction but also contributes to increased retention, as employees are more likely to remain with organizations that invest in their growth and development.
Better succession planning and talent pipeline: Competency models can be used to identify high-potential employees and develop targeted development plans to prepare them for future leadership roles. By understanding the competencies required for success at various organizational levels, HR professionals can proactively nurture talent and ensure a robust pipeline of qualified candidates for critical positions.
Stronger organizational alignment: By clearly defining the skills, knowledge, and behaviors necessary for success across various roles and functions, competency models facilitate better alignment between employees, teams, and the organization’s overall strategic objectives. This alignment enables organizations to achieve greater synergy, efficiency, and effectiveness in pursuing their goals.
In conclusion, competency models offer a wide range of benefits that contribute to the success of both organizations and employees. By defining and organizing essential competencies for various roles and functions, competency models can enhance hiring processes, employee development, performance management, engagement, retention, succession planning, and overall organizational alignment. These benefits ultimately lead to improved organizational performance and a stronger, more adaptable workforce.
Key components of the Competency Model
A well-designed competency model consists of several key components that work together to provide a comprehensive understanding of the skills, knowledge, and behaviors required for success in specific roles or job functions within an organization. These components can be grouped into the following categories:
Core Competencies: These are the foundational skills, knowledge, and behaviors that are essential for success across all roles and functions within the organization. Core competencies typically reflect the organization’s culture, values, and strategic objectives, and may include elements such as communication, teamwork, adaptability, and problem-solving. By establishing a set of core competencies, organizations can promote a consistent and cohesive approach to talent management, ensuring that all employees contribute to the overall success of the organization.
Job-Specific Competencies: These are the competencies that are unique to a particular role or job function, and encompass the specific skills, knowledge, and behaviors required for success in that position. Job-specific competencies may include technical skills, such as programming languages for a software developer, or industry-specific knowledge, such as regulations and best practices for a financial analyst. By defining job-specific competencies, organizations can ensure that employees have the necessary expertise to perform their roles effectively and contribute to the achievement of departmental and organizational goals.
Leadership Competencies: These are the skills, knowledge, and behaviors that are critical for success in leadership roles within the organization. Leadership competencies may include strategic thinking, decision-making, emotional intelligence, and the ability to inspire and motivate others. By identifying and developing leadership competencies, organizations can cultivate a strong pipeline of leaders who are prepared to guide the organization through change and drive long-term success.
Functional Competencies: These are the competencies that are required for success within a specific functional area, such as marketing, finance, or human resources. Functional competencies may encompass specialized skills, knowledge, or behaviors that are relevant across multiple roles within a particular function, and can help organizations ensure consistency and alignment in their approach to talent management within each functional area.
Levels of Proficiency: Competency models often include different levels of proficiency for each competency, providing a clear framework for assessing an individual’s current performance and potential for growth. Proficiency levels may range from basic or foundational to advanced or expert, and can help organizations and employees set realistic expectations for performance and development, as well as identify opportunities for growth and advancement.
Behavioral Indicators: To make the competency model more actionable and relevant, it’s essential to include behavioral indicators for each competency. These indicators are specific, observable actions or behaviors that demonstrate the effective application of a competency in the workplace. By providing clear examples of what each competency looks like in practice, behavioral indicators can help employees better understand the expectations associated with their roles and facilitate more accurate and objective performance evaluations.
In summary, the key components of a competency model include core competencies, job-specific competencies, leadership competencies, functional competencies, levels of proficiency, and behavioral indicators. By defining and organizing these components, organizations can create a comprehensive and effective competency model that serves as a valuable tool for talent management, employee development, and organizational success.
Why is a Competency Model an important tool for Human Resources
A competency model is an important tool for Human Resources (HR) because it provides a structured framework that outlines the essential skills, knowledge, and behaviors required for success in various roles and job functions within an organization. Implementing a competency model in HR processes has several advantages that can significantly enhance talent management, employee development, and overall organizational performance. Here are some key reasons why a competency model is essential for HR professionals:
Effective recruitment and selection: Competency models can inform job descriptions, interview questions, and candidate assessment tools, ensuring that the hiring process is focused on selecting candidates who possess the necessary competencies for a specific role. This leads to more efficient recruitment, improved workforce quality, and reduced turnover.
Targeted employee development: By identifying skill gaps among employees and highlighting the areas that require improvement, competency models enable HR professionals to design targeted training and development programs. This ensures that employees receive the support they need to enhance their skills and knowledge in areas most relevant to their roles, leading to improved performance and career growth.
Streamlined performance management: Competency models provide a clear framework for evaluating employee performance and establishing expectations. This enables HR professionals to develop more objective and transparent performance evaluation criteria, fostering a fair and consistent approach to performance management and feedback.
Enhanced employee engagement and retention: When employees understand the expectations of their roles and have access to opportunities for growth and development, they are more likely to be engaged in their work. Competency models help HR professionals create a supportive environment that promotes employee satisfaction, which, in turn, contributes to increased retention and reduced turnover costs.
Succession planning and talent pipeline development: Competency models can be used to identify high-potential employees and develop targeted development plans to prepare them for future leadership roles. This helps HR professionals proactively nurture talent, ensuring a strong pipeline of qualified candidates for critical positions and contributing to the long-term success of the organization.
Organizational alignment and goal achievement: Competency models foster better alignment between employees, teams, and the organization’s strategic objectives. By clearly defining the skills, knowledge, and behaviors required for success, competency models enable HR professionals to ensure that the workforce is equipped to contribute effectively to the organization’s goals.
Customizable and adaptable approach: Competency models can be tailored to suit the unique needs and culture of an organization, ensuring that the framework is relevant and applicable to the specific context. This flexibility allows HR professionals to adapt the model as the organization evolves or as new challenges and opportunities emerge.
In summary, a competency model is a crucial tool for HR professionals because it offers a structured and systematic approach to talent management, employee development, and performance management. By implementing a competency model in their processes, HR professionals can improve recruitment, employee development, engagement, retention, and overall organizational alignment, ultimately contributing to the long-term success and growth of the organization.
Developing a Competency Model
Creating a competency model is a systematic process that involves identifying and organizing the essential skills, knowledge, and behaviors required for success in specific roles or job functions within an organization. The process of developing a competency model may vary depending on the organization’s size, industry, and strategic objectives. However, the following steps outline a general approach to creating an effective competency model:
Define the purpose and scope: Begin by clarifying the objectives of the competency model, such as improving talent management, enhancing employee development, or supporting strategic goals. Identify the roles, job functions, or organizational levels that the model will cover, and consider the organization’s unique culture, values, and context when defining the scope.
Conduct a job analysis: Perform a thorough job analysis for each role or job function included in the scope of the competency model. This involves gathering information on the tasks, responsibilities, skills, knowledge, and behaviors required for success in each position. Job analysis can be conducted using various methods, such as interviews, surveys, focus groups, or observations of employees performing their jobs.
Identify key competencies: Based on the information gathered during the job analysis, identify the core competencies required for success across all roles and functions, as well as the job-specific, leadership, and functional competencies relevant to each position. Ensure that the competencies are comprehensive, relevant, and aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives.
Define levels of proficiency and behavioral indicators: For each competency, establish different levels of proficiency, ranging from basic or foundational to advanced or expert. This provides a clear framework for assessing employee performance and potential for growth. Additionally, develop specific, observable behavioral indicators for each competency to help employees understand the expectations associated with their roles and to facilitate more accurate and objective performance evaluations.
Validate the competency model: Gather feedback from stakeholders, such as employees, managers, and subject matter experts, to ensure that the competency model accurately reflects the skills, knowledge, and behaviors required for success in each role or job function. Make any necessary revisions based on the feedback received, and ensure that the model remains aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives and culture.
Implement the competency model: Integrate the competency model into various HR processes, such as recruitment and selection, employee development, performance management, and succession planning. This may involve updating job descriptions, developing assessment tools, designing targeted training programs, or revising performance evaluation criteria.
Monitor, evaluate, and update the model: Regularly review the effectiveness of the competency model in achieving its objectives, and gather feedback from stakeholders to identify areas for improvement. As the organization evolves or as new challenges and opportunities emerge, update the competency model to ensure that it remains relevant and effective in supporting the organization’s strategic goals.
In summary, creating a competency model is a systematic process that involves defining the purpose and scope, conducting a job analysis, identifying key competencies, defining levels of proficiency and behavioral indicators, validating the model, implementing it in HR processes, and regularly monitoring, evaluating, and updating the model. By following these steps, organizations can develop a comprehensive and effective competency model that serves as a valuable tool for talent management, employee development, and overall organizational success.
Who should be member of the design team?
Creating a successful competency model requires input from a diverse group of stakeholders to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the necessary skills, knowledge, and behaviors required for various roles and job functions. An ideal design team should be composed of individuals who have the expertise, experience, and perspectives needed to develop an accurate and relevant model. Here are some suggestions for the ideal composition of a competency model design team:
Human Resources professionals: HR professionals bring expertise in talent management, employee development, performance management, and other HR processes. They play a crucial role in integrating the competency model into various HR functions and ensuring alignment with the organization’s strategic objectives.
Subject Matter Experts (SMEs): SMEs possess deep knowledge and expertise in specific job functions, roles, or industries. They can provide valuable insights into the technical and job-specific competencies required for success in their areas of expertise.
Managers and Supervisors: Managers and supervisors have firsthand experience with the skills, knowledge, and behaviors necessary for successful performance in their respective teams or departments. They can provide input on job-specific and leadership competencies, as well as offer practical insights into how the model can be used for performance management and employee development.
Employees: Including employees from various roles and levels within the organization can help ensure that the competency model accurately reflects the expectations and requirements of different positions. Employees can provide valuable feedback on the competencies they believe are crucial for success in their roles, as well as their perspectives on the levels of proficiency and behavioral indicators.
Organizational Development or Learning and Development professionals: These professionals have expertise in employee training, development, and organizational change. They can help design targeted training programs and development initiatives that align with the competency model, and provide input on how the model can be integrated into the organization’s learning and development strategy.
Executive Leadership: Involving executive leaders in the design process can help ensure that the competency model aligns with the organization’s strategic objectives, culture, and values. Executive leaders can provide guidance on core competencies and leadership competencies that are crucial for driving the organization’s long-term success.
External Consultants (optional): In some cases, organizations may choose to engage external consultants with expertise in competency model development. These consultants can offer additional perspectives, best practices, and industry-specific knowledge that can enhance the overall quality and effectiveness of the competency model.
The ideal composition of a competency model design team should include human resources professionals, subject matter experts, managers, employees, organizational development or learning and development professionals, executive leadership, and possibly external consultants. By involving a diverse group of stakeholders with relevant expertise, experience, and perspectives, organizations can create a comprehensive and effective competency model that accurately reflects the skills, knowledge, and behaviors required for success in various roles and job functions.
Implementing a Competency Model
Implementing a competency model involves integrating the identified competencies into various HR processes, such as recruitment and selection, employee development, performance management, and succession planning. The goal is to align the organization’s talent management strategies with the competencies required for success in different roles and job functions. Here is a detailed guide to implementing a competency model in your organization:
Communicate the model: Begin by communicating the purpose, objectives, and benefits of the competency model to stakeholders, such as employees, managers, and executive leadership. Clearly explain how the model will be used in various HR processes and how it will contribute to the organization’s strategic goals. This will help create buy-in and ensure that all stakeholders understand the value of the competency model.
Train HR professionals and managers: Provide training to HR professionals and managers on how to use the competency model in their respective functions, such as recruitment, employee development, performance management, and succession planning. This will ensure that they have the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively implement the model in their day-to-day activities.
Integrate the model into recruitment and selection: Update job descriptions, interview questions, and candidate assessment tools to align with the competencies identified in the model. This will help ensure that the hiring process focuses on selecting candidates who possess the necessary skills, knowledge, and behaviors for success in specific roles.
Develop targeted training and development programs: Based on the competency model, design training and development programs that address the skill gaps among employees and focus on the areas that require improvement. By providing targeted training opportunities, you can help employees enhance their skills and knowledge in areas most relevant to their roles, leading to improved performance and career growth.
Revise performance management processes: Integrate the competency model into performance management processes by establishing clear expectations for employee performance based on the competencies, levels of proficiency, and behavioral indicators. This will help create a more objective and transparent approach to performance evaluation, feedback, and goal-setting.
Align succession planning and talent pipeline development: Use the competency model to identify high-potential employees and develop targeted development plans to prepare them for future leadership roles. This will help ensure a strong pipeline of qualified candidates for critical positions and contribute to the long-term success of the organization.
Monitor and evaluate the implementation: Regularly review the effectiveness of the competency model in achieving its objectives, such as improving talent management, enhancing employee development, or supporting strategic goals. Gather feedback from stakeholders, including employees, managers, and executive leadership, to identify areas for improvement and make any necessary adjustments to the model or its implementation.
Update the model as needed: As the organization evolves, or as new challenges and opportunities emerge, update the competency model to ensure that it remains relevant and effective in supporting the organization’s strategic goals. This may involve revising competencies, levels of proficiency, or behavioral indicators, as well as updating the HR processes that incorporate the competency model.
Implementing a competency model involves communicating the model to stakeholders, training HR professionals and managers, integrating the model into various HR processes, developing targeted training and development programs, revising performance management processes, aligning succession planning and talent pipeline development, monitoring and evaluating the implementation, and updating the model as needed. By following these steps, organizations can effectively implement a competency model that serves as a valuable tool for talent management, employee development, and overall organizational success.
Conclusion
In conclusion, competency models play a critical role in enhancing talent management, employee development, and overall organizational performance. By providing a structured framework that outlines the essential skills, knowledge, and behaviors required for success in various roles and job functions, competency models enable organizations to make informed decisions related to recruitment, training, performance management, and succession planning.
To develop a comprehensive and effective competency model, organizations should begin by defining the purpose and scope, conducting a thorough job analysis, identifying key competencies, defining levels of proficiency and behavioral indicators, and validating the model with input from diverse stakeholders. The ideal design team should include HR professionals, subject matter experts, managers, employees, organizational development or learning and development professionals, executive leadership, and possibly external consultants. This diverse group of stakeholders can ensure that the model accurately reflects the skills, knowledge, and behaviors required for success in various roles and job functions.
Once the competency model is created, organizations must effectively implement it by communicating its purpose and objectives to stakeholders, training HR professionals and managers, and integrating the model into various HR processes, such as recruitment and selection, employee development, performance management, and succession planning. Organizations should also regularly monitor, evaluate, and update the competency model to ensure that it remains relevant and effective in supporting the organization’s strategic goals.
Implementing a well-designed competency model can lead to numerous benefits, including more efficient recruitment processes, targeted employee development programs, streamlined performance management, increased employee engagement and retention, effective succession planning, and overall organizational alignment with strategic objectives. By following the steps outlined in this article, organizations can develop and implement a competency model that serves as a valuable tool for driving long-term success and growth.
In an ever-changing business landscape, it is crucial for organizations to continuously adapt and invest in the development of their workforce. Competency models provide a solid foundation for organizations to align their talent management strategies with their strategic objectives, ensuring that employees possess the necessary skills, knowledge, and behaviors to contribute effectively to the organization’s success. By embracing competency models, organizations can cultivate a high-performing and agile workforce capable of navigating the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.